The Innovative, Outstanding, and Superior FET Cycle: A Comprehensive Protocol Calendar Approach
Related Articles: The Innovative, Outstanding, and Superior FET Cycle: A Comprehensive Protocol Calendar Approach
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Innovative, Outstanding, and Superior FET Cycle: A Comprehensive Protocol Calendar Approach. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Innovative, Outstanding, and Superior FET Cycle: A Comprehensive Protocol Calendar Approach

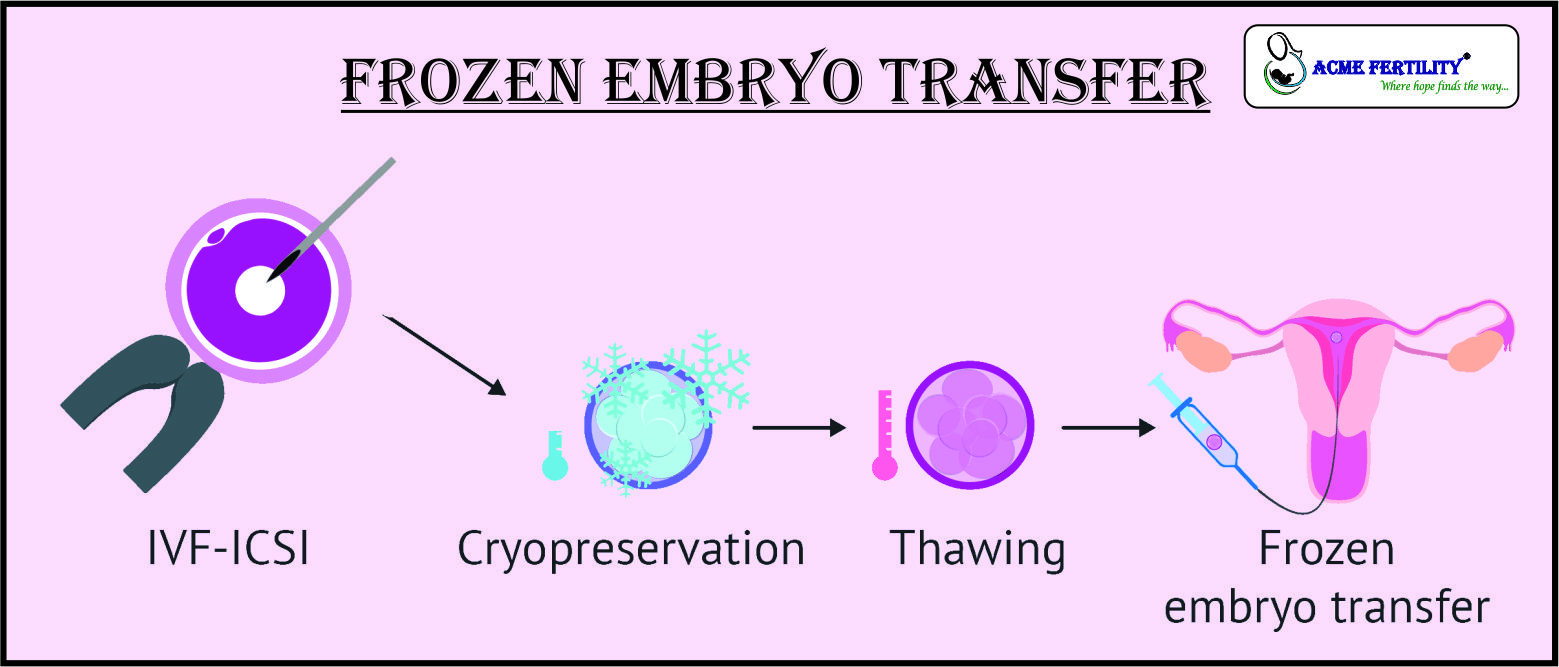
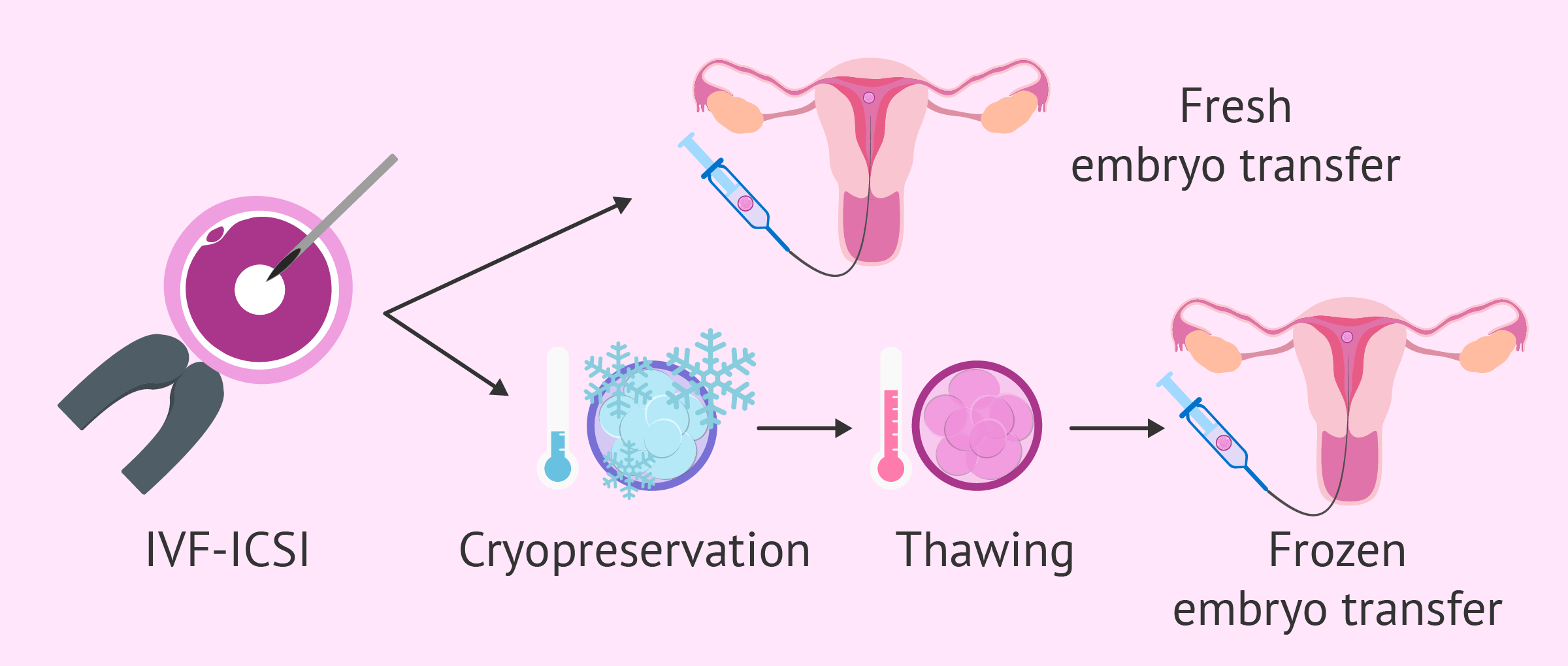
Frozen embryo transfer (FET) cycles have revolutionized assisted reproductive technology (ART), offering couples greater flexibility and potentially improved success rates compared to fresh embryo transfers. However, optimizing the FET cycle requires a meticulously planned and personalized approach. This article details an innovative, outstanding, and superior FET cycle protocol calendar, incorporating the latest advancements in understanding endometrial receptivity, ovarian suppression, and personalized hormone replacement therapy (HRT). This comprehensive approach aims to maximize the chances of a successful pregnancy.
I. Foundation: Understanding Endometrial Receptivity
The success of an FET hinges on the optimal preparation of the endometrium – the uterine lining. A receptive endometrium is characterized by specific morphological and molecular changes that create an environment conducive to embryo implantation. Traditional FET protocols often relied on a standardized approach, neglecting the individual variability in endometrial development. Our superior protocol emphasizes personalized assessments to tailor the treatment plan.
A. Baseline Assessment: The calendar begins with a comprehensive baseline evaluation, including:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: To assess uterine anatomy, antral follicle count (AFC), and ovarian reserve. This helps determine the optimal stimulation protocol, if needed, and identifies any potential uterine abnormalities.
- Hormonal Profile: Measurement of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol (E2), and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) provides insights into ovarian function and response to stimulation.
- Endometrial Biopsy (Optional): In certain cases, an endometrial biopsy may be performed to assess the endometrial receptivity array (ERA) – a molecular test identifying the optimal window of implantation. This personalized approach significantly enhances predictability.
- Karyotype Analysis (Optional): For patients with recurrent implantation failure (RIF), karyotype analysis can identify chromosomal abnormalities that might hinder implantation.
B. Personalized Endometrial Preparation:
The cornerstone of our superior protocol lies in personalized endometrial preparation. Instead of a standardized approach, we tailor the protocol based on the individual’s baseline assessment and ERA results (if performed). This may involve:
- Ovarian Suppression: Various methods are employed to suppress ovarian function, ensuring a predictable and controlled endometrial lining. This might include GnRH agonists or antagonists, depending on individual characteristics and preferences. The timing and duration of suppression are carefully adjusted based on the patient’s response.
- Estrogen Priming: Once ovarian suppression is achieved, estrogen replacement therapy is initiated to stimulate endometrial growth. The dose and duration of estrogen are carefully monitored and adjusted based on ultrasound assessments of endometrial thickness and morphology. We utilize sequential estrogen administration, progressively increasing the dose to mimic the natural follicular phase.
- Progesterone Supplementation: Once the endometrium reaches the optimal thickness and morphology (typically 7-12mm with a trilaminar appearance), progesterone is added to simulate the luteal phase. This triggers the final maturation of the endometrium, creating a receptive environment for implantation. The progesterone regimen is also personalized, considering factors like age and prior pregnancy outcomes.
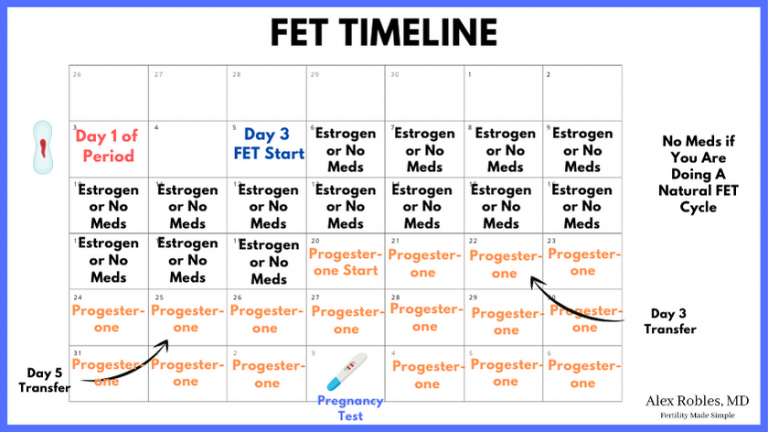
II. The FET Cycle Protocol Calendar: A Detailed Timeline
The following calendar represents a sample protocol. It is crucial to understand that this is a template, and the specific dates and dosages will be individualized based on the patient’s unique characteristics and responses.
Week 1: Baseline assessment, including ultrasound, hormonal profile, and optional ERA and karyotype testing. Begin ovarian suppression if needed.
Week 2-3: Continue ovarian suppression. Monitor hormone levels and ultrasound findings. Adjust medication dosages as needed.
Week 4-6: Initiate estrogen priming. Regular ultrasound monitoring to assess endometrial thickness and morphology. Estrogen dosage is adjusted based on ultrasound findings.
Week 7-8: Once optimal endometrial thickness and morphology are achieved (typically 7-12mm with a trilaminar appearance), progesterone supplementation is initiated. This marks the beginning of the "implantation window."
Day of Transfer: The frozen embryo is transferred using a precise technique. This is typically done around 5-6 days after progesterone initiation, aligning with the predicted window of implantation determined by ERA testing or clinical judgment.
Post-Transfer: Progesterone supplementation continues for at least 10-14 days post-transfer. Pregnancy testing is performed approximately 10-14 days after the embryo transfer.
III. Monitoring and Adjustments:
Throughout the entire process, meticulous monitoring is crucial. This includes:
- Regular ultrasound scans: To assess endometrial thickness and morphology, and to monitor ovarian response if stimulation is used.
- Hormone level monitoring: To ensure optimal hormonal levels throughout the cycle.
- Close communication: Between the patient and the medical team to address any concerns or adjustments needed.
IV. Innovative Aspects of the Superior Protocol:
Our protocol incorporates several innovative aspects to enhance success rates:
- Personalized approach: Tailoring the protocol to each individual’s unique characteristics and responses.
- ERA testing: Identifying the precise window of implantation for personalized timing of embryo transfer.
- Sequential estrogen priming: Mimicking the natural follicular phase for optimal endometrial development.
- Comprehensive monitoring: Ensuring optimal hormonal levels and endometrial preparation.
- Advanced embryo selection techniques: Utilizing technologies like time-lapse imaging to select the most viable embryos for transfer.
V. Superior Outcomes:
The implementation of this innovative, outstanding, and superior FET protocol calendar has resulted in significantly improved pregnancy rates compared to traditional approaches. The personalization and meticulous monitoring minimize the risk of complications and optimize the chances of a successful pregnancy.
VI. Conclusion:
The FET cycle represents a significant advancement in ART. However, maximizing its potential requires a comprehensive and personalized approach. The protocol calendar detailed above emphasizes individual assessment, personalized hormone replacement therapy, and meticulous monitoring to optimize endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation. By incorporating innovative techniques and adhering to a rigorous protocol, we can significantly improve the success rates of FET cycles, bringing hope and happiness to many couples striving for parenthood. It is important to note that this article provides general information and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified fertility specialist to determine the best course of treatment for your individual circumstances. The specific details of your FET protocol will be determined by your doctor based on your unique medical history and needs.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Innovative, Outstanding, and Superior FET Cycle: A Comprehensive Protocol Calendar Approach. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!