difference between fiscal year and calendar year Conclusive Consequent Certain
Related Articles: difference between fiscal year and calendar year Conclusive Consequent Certain
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to difference between fiscal year and calendar year Conclusive Consequent Certain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Fiscal Year vs. Calendar Year: A Comprehensive Comparison

The terms "fiscal year" and "calendar year" are frequently used in accounting, finance, and business, often interchangeably, leading to confusion. While both represent a 12-month period used for accounting and reporting purposes, they differ significantly in their starting and ending points, resulting in consequential impacts on financial planning, budgeting, and analysis. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in financial management, investment, or business operations. This article will provide a conclusive and certain examination of the distinctions between fiscal and calendar years, exploring their implications across various contexts.
Defining the Terms:
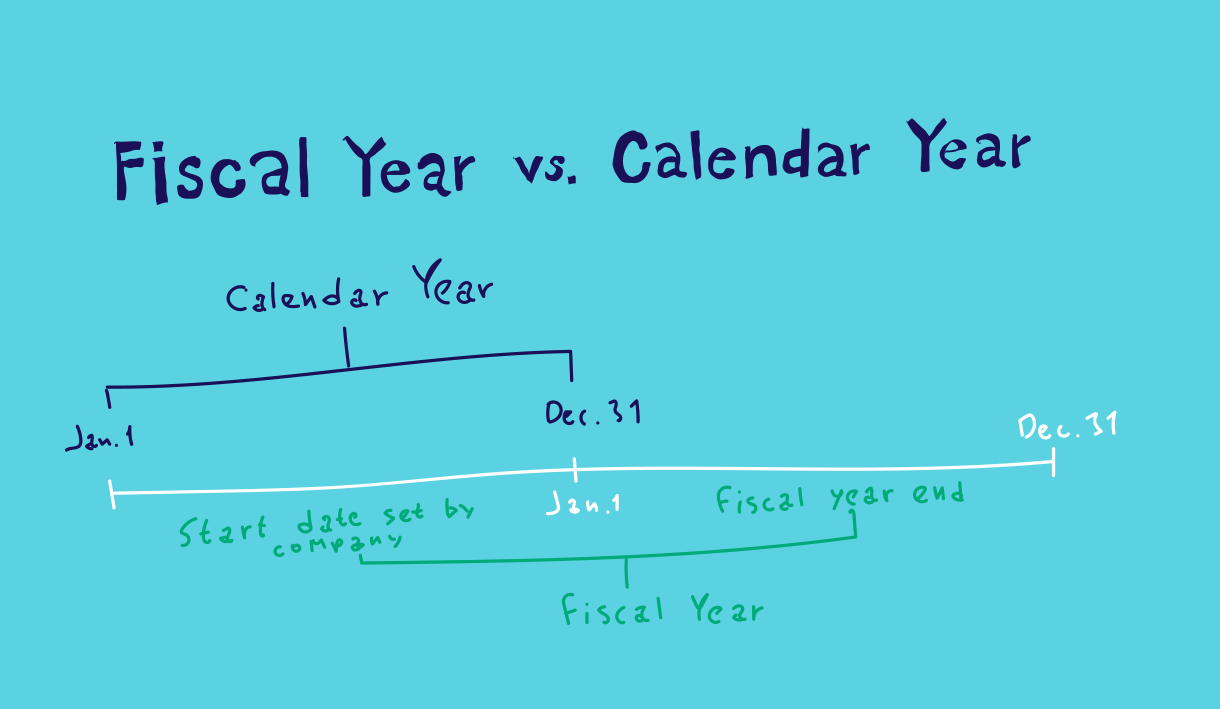
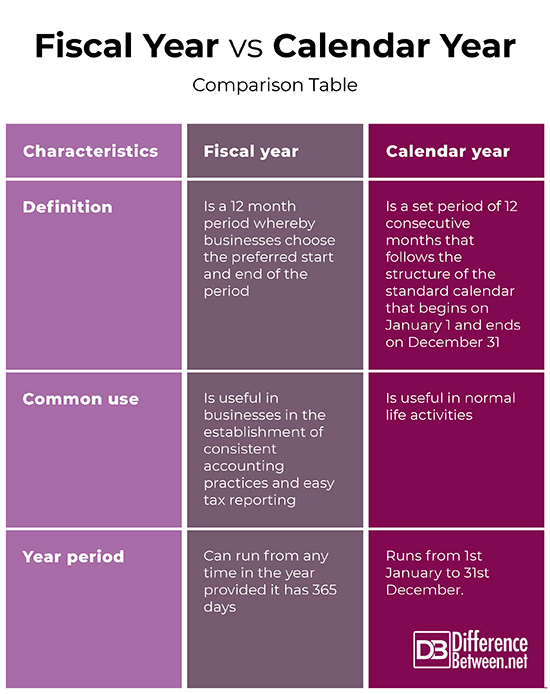
The calendar year is universally recognized as a 12-month period starting on January 1st and ending on December 31st. Its simplicity and widespread adoption make it the standard for many personal and social activities, as well as for certain businesses. However, its alignment with seasonal fluctuations can introduce complexities in financial reporting for businesses with uneven revenue streams throughout the year.
A fiscal year, on the other hand, is a 12-month period that a company or government uses for accounting purposes. Unlike the calendar year, the fiscal year’s start and end dates are not fixed. They can begin on any date and are chosen strategically based on factors specific to the organization. This flexibility allows businesses to better reflect their operational cycles and align their financial reporting with their peak seasons, production cycles, or other relevant factors.
Why the Difference Matters: A Conclusive Analysis
The choice between a fiscal year and a calendar year has significant implications for several key aspects of financial management:
-
Accurate Financial Reporting: A fiscal year allows businesses to structure their financial reporting to better reflect their operational reality. For example, a retail business might choose a fiscal year that aligns with its peak holiday shopping season (e.g., November 1st to October 31st), making it easier to assess year-end performance accurately. Using a calendar year would obscure this crucial seasonal influence on sales and profits. Similarly, a company with a manufacturing process that involves significant seasonal factors (e.g., agricultural products) will find a fiscal year better suited for accurate reflection of their operational performance.
-
Improved Budgeting and Forecasting: A strategically chosen fiscal year facilitates more effective budgeting and forecasting. By aligning the fiscal year with the business’s natural operational rhythm, companies can create more realistic budgets and forecasts that better reflect expected revenues and expenses. This improved accuracy leads to better resource allocation, reduced financial risks, and enhanced profitability. A calendar year might lead to inaccurate forecasting if the business’s operational cycle doesn’t align with the January-December timeframe.
-
Simplified Tax Compliance: While the timing of tax filing deadlines might still be tied to the calendar year, the use of a fiscal year can simplify the process of compiling financial information for tax purposes. The organization’s financial data will more accurately reflect the business’s performance over a period consistent with its operational cycle, resulting in a more straightforward tax preparation process.
-
Enhanced Internal Control and Management: Using a fiscal year that matches the company’s operational rhythm enhances internal control and management. Regular reporting based on this aligned period provides a more accurate picture of the company’s financial health and operational efficiency, leading to improved decision-making and proactive management of potential issues.
-
Comparability of Financial Statements: While companies using different fiscal years can make comparisons challenging, using a consistent fiscal year over time allows for meaningful internal comparisons of performance across different periods. This longitudinal analysis is crucial for identifying trends, assessing the effectiveness of strategies, and making informed decisions regarding future operations.
Consequent Impacts Across Different Sectors:
The implications of choosing a fiscal year versus a calendar year vary across different sectors:
-
Retail: Retail businesses often opt for fiscal years that encompass their peak holiday shopping seasons, providing a clearer picture of annual performance. This allows them to better assess the effectiveness of holiday promotions and plan for the coming year.
-
Agriculture: Agricultural businesses frequently adopt fiscal years aligned with their planting and harvesting cycles. This aligns their financial reporting with their production cycle, allowing for a more accurate assessment of profitability and operational efficiency.
-
Government: Government fiscal years often differ from the calendar year, dictated by legislative cycles or budgetary considerations. The fiscal year’s end date might coincide with the end of a legislative session or a specific budgetary period.
-
Education: Educational institutions often align their fiscal year with the academic year, making it easier to manage budgets and track expenses related to student enrollment, tuition payments, and operational costs.
Certain Considerations for Choosing a Fiscal Year:
The decision of whether to use a fiscal year or a calendar year is not arbitrary. Several factors should be considered:
-
Industry norms: Certain industries have established conventions regarding the use of fiscal years. Understanding these norms can help businesses align their practices with industry standards and facilitate comparisons with competitors.
-
Business cycle: The natural cycle of the business, including peak seasons, production cycles, and major operational events, should be the primary determinant of the fiscal year’s start and end dates.
-
Tax implications: While the choice of fiscal year doesn’t directly affect tax rates, it can influence the timing of tax payments and the complexity of tax preparation.
-
Reporting requirements: Regulatory requirements and reporting deadlines for financial statements might influence the choice of fiscal year to ensure compliance.
-
Internal control and management: The fiscal year should be chosen to optimize internal control and management processes, ensuring effective monitoring of financial performance and operational efficiency.
Conclusion:
The choice between a fiscal year and a calendar year is a significant decision with far-reaching consequences for financial management, budgeting, and reporting. While the calendar year offers simplicity and widespread recognition, the flexibility of a fiscal year allows businesses to tailor their financial reporting to better reflect their operational cycles and enhance the accuracy of financial planning and analysis. Understanding the differences between these two accounting periods is crucial for anyone involved in financial management, investment, or business operations, enabling them to make informed decisions that contribute to the long-term success of their organization. The strategic selection of a fiscal year, based on a thorough consideration of the factors discussed above, is essential for achieving accurate financial reporting, effective budgeting, and ultimately, improved profitability and operational efficiency. The conclusive evidence presented underscores the critical importance of aligning the accounting period with the organization’s operational reality for optimal financial management.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into difference between fiscal year and calendar year Conclusive Consequent Certain. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!